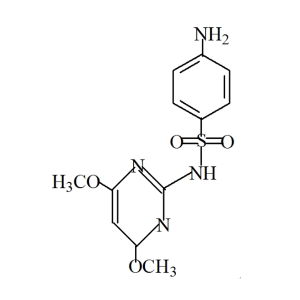
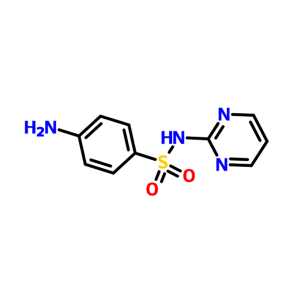
Sulfamethazine
Physical and chemical properties
Density: 1.392g/cm3
Melting point: 197°C
Boiling point: 526.2ºC
Flash point: 272.1ºC
Appearance: white crystalline powder
Solubility: almost insoluble in water, insoluble in ether, easily soluble in dilute acid or dilute alkali solution
Sulfadiazine is a sulfanilamide antibiotic with similar antibacterial spectrum to sulfadiazine. It has antibacterial effects on enterobacteriaceae bacteria such as non-zymogenic Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Salmonella, Shigella, etc. Neisseria gonorrhoea, Neisseria meningitidis and Haemophilus influenzae. However, bacterial resistance to the product increased, especially streptococcus, Neisseria and Enterobacteriaceae bacteria. Sulfonamides are broad-spectrum bacteriostatic agents, similar in structure to p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), which can competitively act on dihydrofolate synthetase in bacteria, thereby preventing PABA from being used as raw material to synthesize folate required by bacteria and reducing the amount of metabolically active tetrahydrofolate. The latter is an essential substance for the synthesis of purines, thymidine nucleosides and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), so it inhibits the growth and reproduction of bacteria.
It is mainly used for mild infections caused by sensitive bacteria, such as acute simple lower urinary tract infection, acute otitis media and skin soft tissue infection.